April 24, 2025
Application of industrial robots in intelligent manufacturing
As industrial intelligence evolves, intelligent manufacturing promotes the development of the robotics industry, while robots drive innovation within intelligent manufacturing.
1 Research Background
China places strong emphasis on developing industrial robots and is actively establishing industrial parks to support their broad application in key manufacturing sectors like automotive, 3C electronics, and metallurgy. Thanks to their high precision, flexibility, and intelligence, industrial robots are playing an increasingly vital role in boosting the competitiveness of intelligent manufacturing.
2 Application characteristics of industrial robots in the field of intelligent manufacturing
2.1 Overall application idea
This paper focuses on designing an intelligent manufacturing production line for oil cylinder pistons and explores how industrial robots are applied in the process. The production line uses a CJ2M-CPU35 PLC and includes two robots—one handles loading in coordination with the CNC machining center, while the other manages workpiece transfer to the inspection unit and subsequent processing stages. The operation process of the intelligent manufacturing production line is shown in Figure 1.
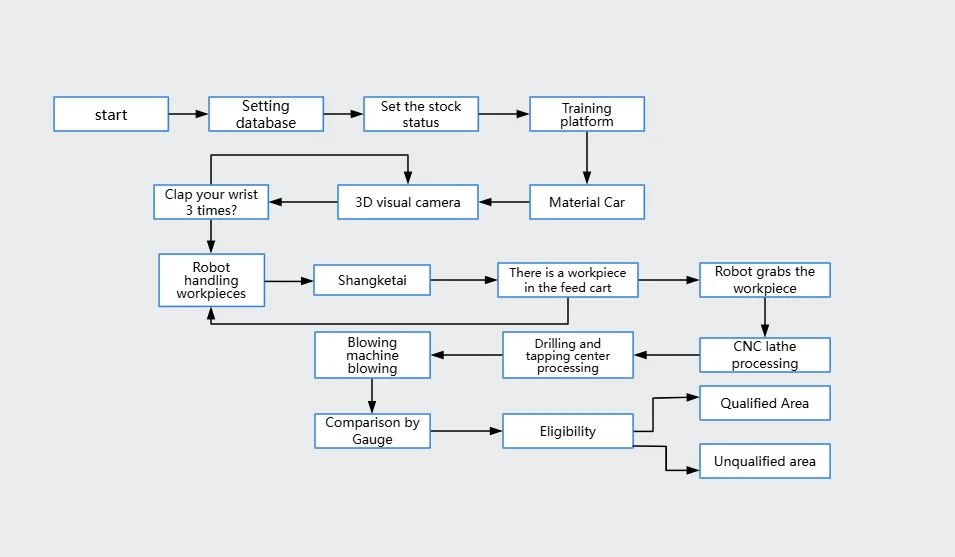
Figure 1: Operation process of the intelligent manufacturing production line
2.2 Machining Center
The machining center of the intelligent manufacturing production line features a CK6146YGx2500 CNC lathe, with its basic parameters listed in Table 1. This CNC lathe establishes an information interaction mechanism with the industrial robot, allowing them to work together and achieve semi-closed-loop control.
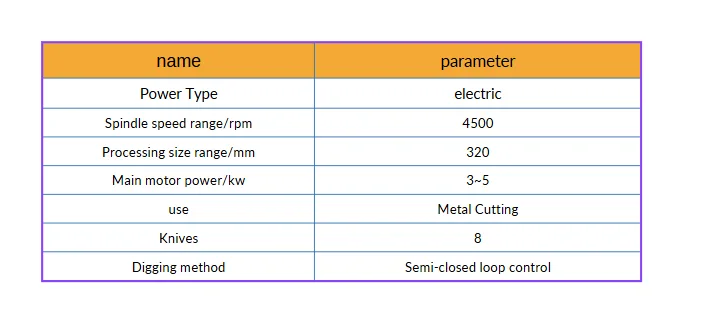
Table 1: Basic parameters of the CNC lathe
2.3 Industrial Robots
Traditional production lines rely on manual labor to complete loading and unloading, and handling. This paper introduces an industrial robot with loading and unloading, and grasping functions to replace manual operations. The robot consists of mechanical, sensing, and drive systems, and its structure is shown in Figure 2.
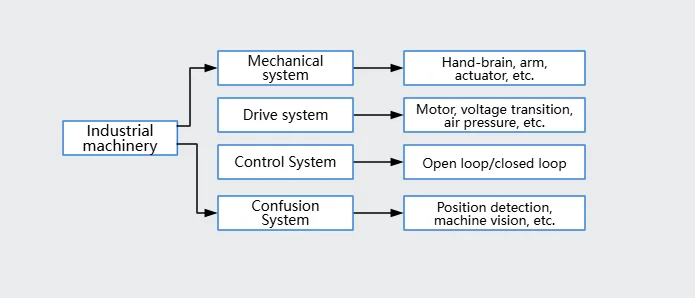
Figure 2: Basic structure of the loading and unloading robot
This article features the Huazhong CNC 612 seven-axis articulated robot, which delivers high-precision grasping and works seamlessly with CNC turning and milling to meet demanding processing requirements.
3. Functional realization of industrial robots in intelligent manufacturing production lines
3.1 Interaction between industrial robots and intelligent manufacturing production lines
In the intelligent manufacturing process, industrial robots handle material loading, unloading, and workpiece transfer. This setup reduces human errors and boosts production efficiency. The robot connects to the PLC through a switch using the EtherNet/IP protocol. After the staff preset the operating parameters, they can control the robot remotely. Once the production line starts, the robot sends a standby request to the PLC. The PLC then follows the host computer’s instructions and sends control commands to the robot.
3.2 Load parameter control of industrial robots
We can calculate the load on the industrial robot during operation using equations (1) and (2). In these equations, J represents the moment of inertia applied to the robot axis, and G indicates the flange load. Jox, Joy, and Joz refer to the moments of inertia relative to the load’s center of gravity. x and y specify the center of gravity’s position in the tool coordinate system. N and M define the maximum allowable moments of inertia for the J5 and J6 axes, respectively.
3.3 Practical Operation of Industrial Robots
In the intelligent manufacturing production line, one industrial robot handles grabbing and transferring workpieces at the material collection and safety points. The second robot takes charge of loading, transporting, and assisting with processing tasks. The system includes two loading points and two safety points. To expand its application range, the processing center and material warehouse each feature a seventh-axis teaching point, enabling more flexible operations. The robot uses a visual system to inspect workpieces and adjust processing parameters in real time, then transfers the finished workpieces to the unloading area.
4 Conclusion
The application of industrial robots in intelligent manufacturing enhances the intelligence level of production lines. By improving operational safety and product quality, robots also help reduce production and processing costs. Therefore, promoting and applying industrial robots in intelligent manufacturing is both practical and necessary.